Last Updated: 2023-10-20 12:20:09 Friday
-- TOC --
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
这段话有点费解:一个名叫height的integer array,这个array中的数字表示height,array的长度为n,这个array模拟了n条垂直线,第i条线的坐标是(i,0)和(i,height[i])。
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water. Return the maximum amount of water a container can store. Notice that you may not slant the container.
找到两条垂线,结合x轴,形成一个矩形区域,目标是使得这个矩形区域的面积最大,返回最大值。(假设这个矩形框用来装水,上面那条横线也需要是水平的)
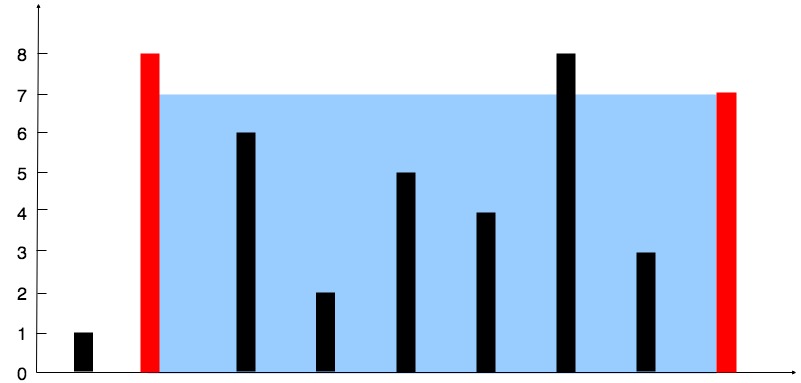
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water the container can contain is 49 (7x7).
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1 (1x1)
约束条件平平无奇:
- n == height.length
- 2 <= n <= 10^5
- 0 <= height[i] <= 10^4
题目有个图,对理解这个问题有帮助:

通过遍历x轴,两重循环,可以遍历出所有的container大小,最后一定可以得到一个最大值,但这是个\(O(N^2)\)的解法。
用Python写完后submit,TLE!(Time Limit Exceeded)
控制面积有两个维度,width和height,从大到小遍历width时,也在逐渐推高需要的height值,如果需要的height值大于了最大height,此时就可以结束了。
import math
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
max_height = max(height)
num_vlines = len(height)
width = num_vlines - 1
max_area = 0
while True:
for i in range(num_vlines-width):
h = min(height[i],height[i+width])
area = width * h
if area > max_area:
max_area = area
width -= 1
if width == 0:
break
need_height = math.ceil(max_area/width)
if need_height > max_height:
break
return max_area
这个思路比前面的在一般情况下会快一点,但依然是\(O(N^2)\)级别,依然TLE.....:(
在一个具有某种顺序的序列中寻找两个点,这两个点的某些属性能够满足某一特定的条件,一般是先取左右两个点,然后逐渐向中间靠拢。复杂度:\(O(N)\)
比如:在一个有序数组里,寻找两个数,让他俩的和等于某个具体的值。LeetCode第1题,我有尝试这个思路的实现。
这一题也可以采用这个思路:虽然height数组没有排序,但是当width缩小后,height必须需要增大,才能够计算出更大的面积。因此,这两个点的变动,就可以按照往height增大的方向进行。
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
max_area = 0
lo = 0
hi = len(height) - 1
while lo < hi:
area = min(height[lo],height[hi]) * (hi-lo)
if area > max_area:
max_area = area
if height[lo] < height[hi]:
lo += 1
else:
hi -= 1
return max_area
#define MIN(a,b) (a<b?a:b)
int maxArea(int* height, int heightSize){
int max = 0;
int lo = 0;
int hi = heightSize - 1;
while(lo < hi){
int area = MIN(height[lo],height[hi]) * (hi-lo);
if(area > max)
max = area;
if(height[lo] > height[hi])
--hi;
else
++lo;
}
return max;
}
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) noexcept{
int n {static_cast<int>(height.size())};
int max {};
int lo {};
int hi {n-1};
while(lo < hi){
int area {min(height[lo],height[hi])*(hi-lo)};
if(area > max)
max = area;
if(height[lo] > height[hi])
--hi;
else
++lo;
}
return max;
}
};
也许用Two Pointer来描述本题的思路,不够准确。本题的得分点是贪心算法,Greedy Algorithm。
所谓Greedy,即在每一步计算过程中,都选择当前最优的解,即贪心!本题首先计算width最大情况下的area,每一步都意味着width在缩小,因此height必须沿着增大的方向更新。本题只是模拟了Two Pointer的代码结构,实际上是贪心算法的内核。
通过每一步计算最优解,来得到最后的结果,这就是贪心算法的思想。如果构建每一步的计算,还需要其它技巧。需要了解,并非所有的问题,都适合使用贪心的策略。
本文链接:https://cs.pynote.net/ag/leetcode/202305182/
-- EOF --
-- MORE --